Scenario
A user reported suspicious activity on their Windows workstation. As a forensic investigator, you've been provided with a disk image and tasked with uncovering the full attack chain by answering a series of questions.
Investigation Process
Initial Triage & System Information
The first step in any forensic investigation is to establish the integrity of the evidence and gather basic system information.
Q1: Disk Image Hash
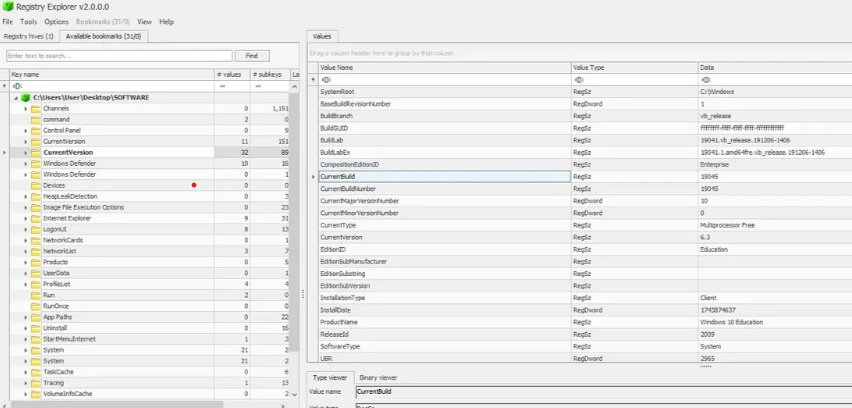
Q2: OS Build Number
Located in the SOFTWARE registry hive:
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersionBuild Number: 19045
Q3: Victim's IP Address
SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\Tcpip\Parameters\InterfacesIP Address: 192.168.206.131
Email Application & User Analysis
Q4: Email Application
Examined the AppData folder to identify installed applications:
Location:
C:\Users\ammar\AppData\Roaming\Thunderbird
sys.exe was discovered in the AppData directory. This is highly unusual as legitimate system executables should be in System32, not in user directories.
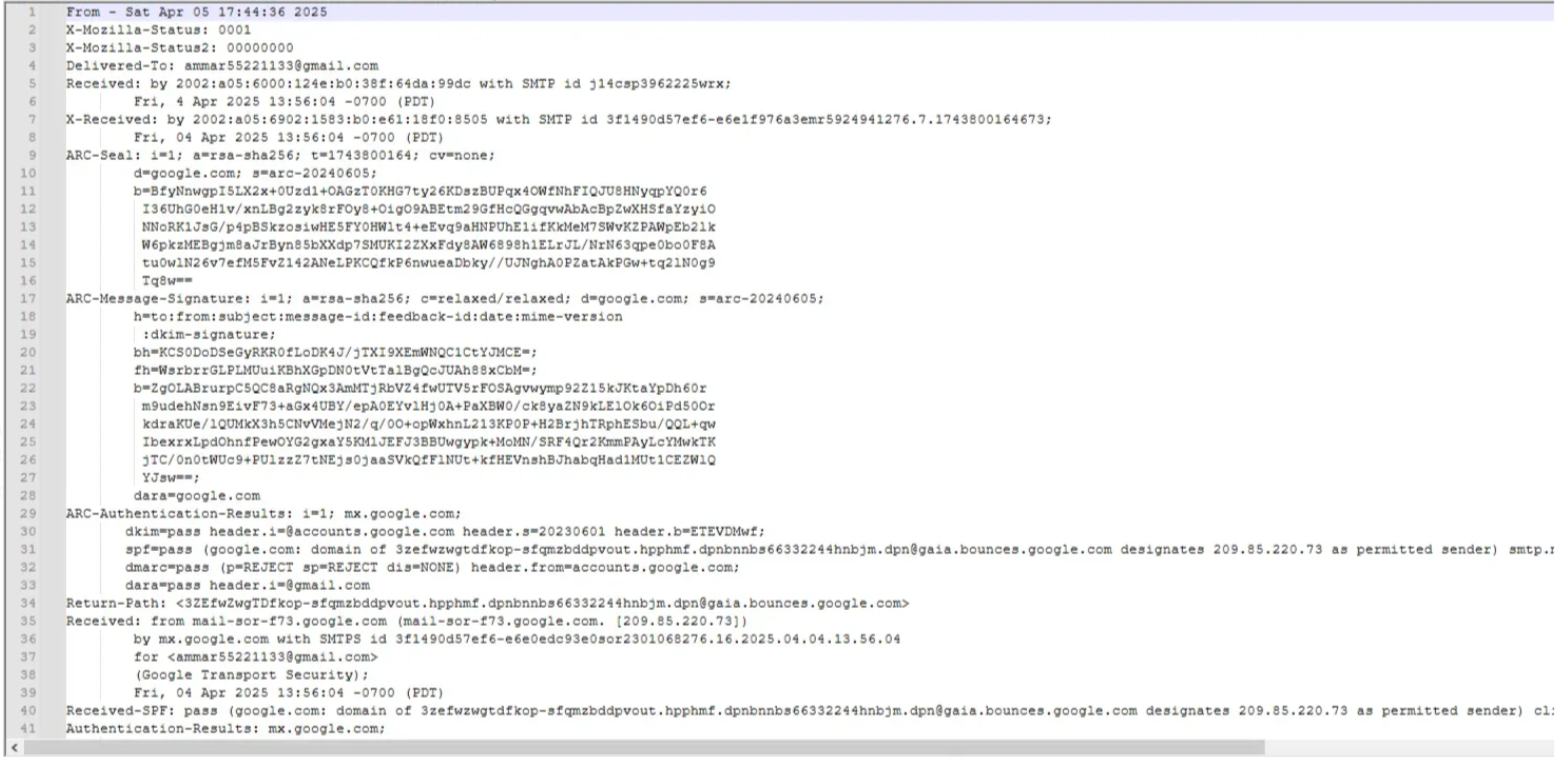
Q5: Victim's Email Address
Navigated to Thunderbird profile: Profiles/6red5uxz.default-release/ImapMail
Identifying the Attack Vector
Q6: Attacker's Email
Analyzed the INBOX file and found suspicious emails from Mohamed Masmoudi containing a GitHub repository link.
Attack Method: Phishing email with malicious GitHub repo
Q7: Malware Delivery URL
Examined the GitHub repository's package.json file:

https://tmpfiles.org/dl/23860773/sys.exe
This npm package automatically downloads and executes the malware upon installation!
Malware Characterization
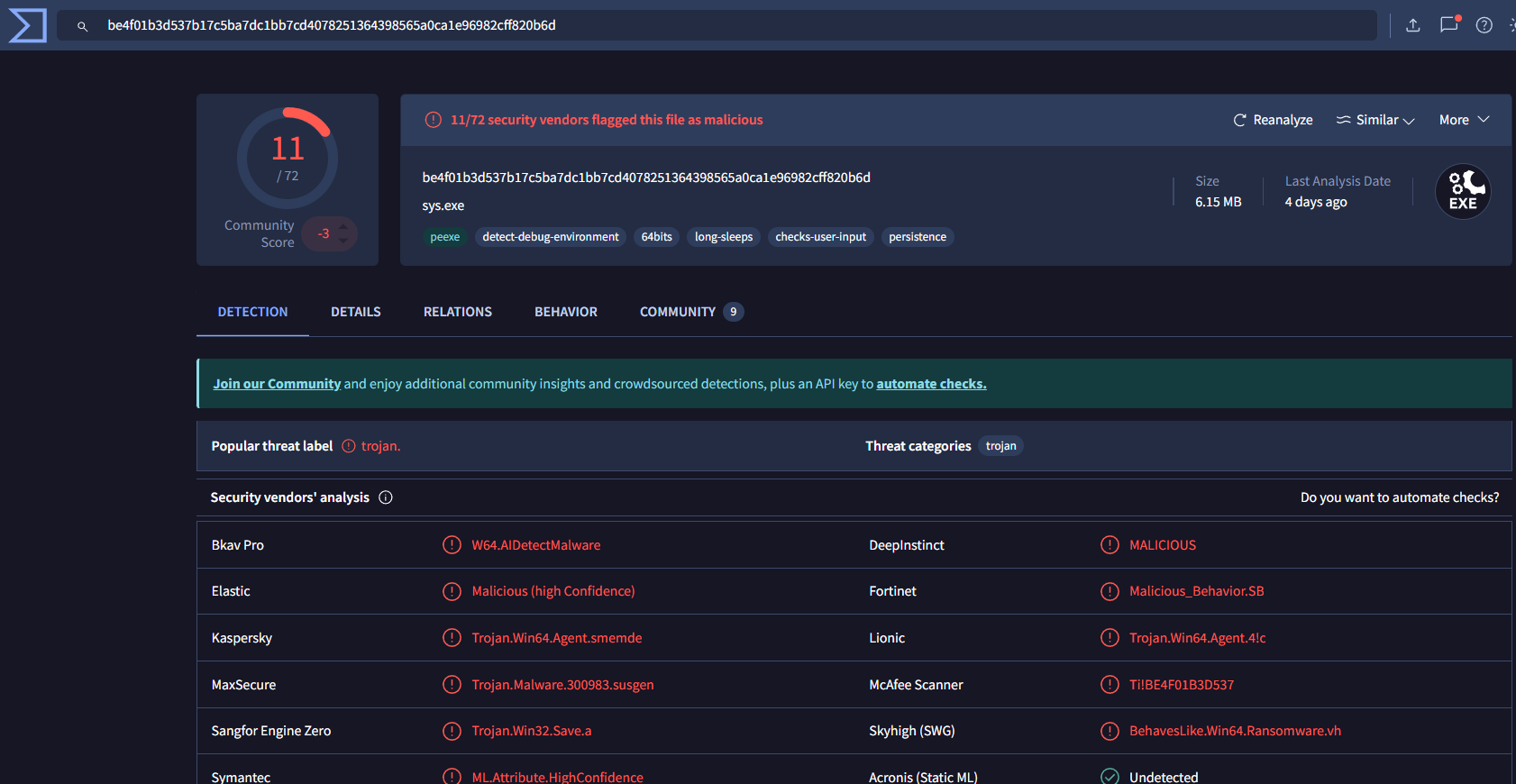
Q8: Malware Hash
Uploaded to VirusTotal for analysis:
Command & Control Infrastructure
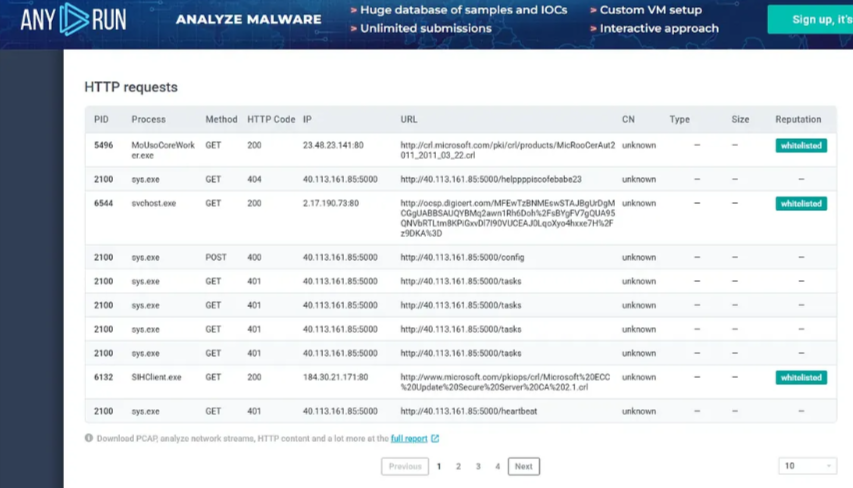
Q9-10: C2 Server Information
Using VirusTotal's behavioral analysis and network indicators:
C2 Port: 5000
Q11: Initial Beacon
Analyzed the malware using any.run sandbox:
Persistence Analysis
Q12: System Fingerprinting
The malware creates a unique identifier file:
C:\Users\Public\Documents\id.txtContent:
3649ba90-266f-48e1-960c-b908e1f28aef
This UUID likely serves as a bot identifier for the C2 server to track infected machines.
Q13-14: Registry Persistence
Exported and analyzed the NTUSER.DAT hive:
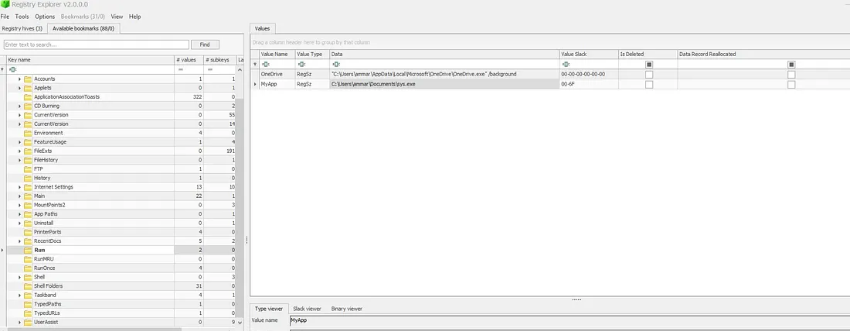
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run\MyAppValue:
C:\Users\ammar\Documents\sys.exe
This ensures the malware automatically executes every time the user logs in.
Q15: Authentication Token
Extracted hardcoded secrets using strings analysis:
e7bcc0ba5fb1dc9cc09460baaa2a6986
Attack Timeline
1. Initial Compromise
Attacker (masmoudim522@gmail.com) sends phishing email to victim (ammar55221133@gmail.com) with link to malicious GitHub repository.
2. Malware Delivery
Victim installs npm package, triggering postinstall script that downloads sys.exe from tmpfiles.org.
3. Initial Execution
Malware executes from AppData directory and creates unique identifier (3649ba90-266f-48e1-960c-b908e1f28aef) in id.txt.
4. Persistence Establishment
Malware creates registry Run key for automatic execution on user login.
5. C2 Communication
Establishes connection with C2 server (40.113.161.85:5000) using hardcoded authentication token.
6. Ongoing Activity
Malware remains persistent, maintaining C2 communication for command execution and data exfiltration.
Key Findings Summary
5
Attack Stages Identified
3
Persistence Mechanisms
1
C2 Server Discovered
Go
Malware Language
Tools & Techniques
Disk Forensics
- FTK Imager
- Registry Explorer
- RegRipper
Malware Analysis
- VirusTotal
- any.run Sandbox
- strings utility
Email Forensics
- Thunderbird Profile Analysis
- MBOX File Parsing
Continue to Next Challenge
Check out the Lost File challenge where we perform memory forensics and cryptographic analysis.